Cadmium Isotope Fractionations Induced by Foliar and Root Uptake for Rice Exposed to Atmospheric Particles: Implications for Environmental Source Tracing
Rice roots and leaves were exposed to cadmium (Cd)-contaminated particles in a greenhouse to modify the fractionation during Cd uptake and transport in the plants by using the Bayesian mixing model. The exposure to atmospheric Cd in rice near a copper smelter was determined under the field conditions. The results showed that the leaves directly absorb and accumulate atmospheric Cd in other aboveground tissues by 84–99%. Positive values of Δ114/110CdLeaf–Particle (0.08–0.11‰), Δ114/110CdNode–Leaf (0.77–0.81‰), and Δ114/110CdGrain–Leaf (0.39–0.43‰)following foliar exposure as well as Δ114/110CdRoot–Particle (0.19–0.22‰) and Δ114/110CdGrain–Root (?0.29 to 0.34‰) following root exposure suggested that particles released heavy isotopes. The roots and leaves preferentially retained light isotopes and transported heavy isotopes upward. The Cd isotope fractionations in the plant were constant under both root and foliar exposures at two dosages. The results were used to correct the parameters in the isotope mixing models and to trace the source of atmospheric Cd in rice tissues in the field. Both models of isotope mixing and mass balance suggested 50–63% Cd deposition on the grains. This study provides a theoretical basis for tracing the source of Cd isotopes in plants.
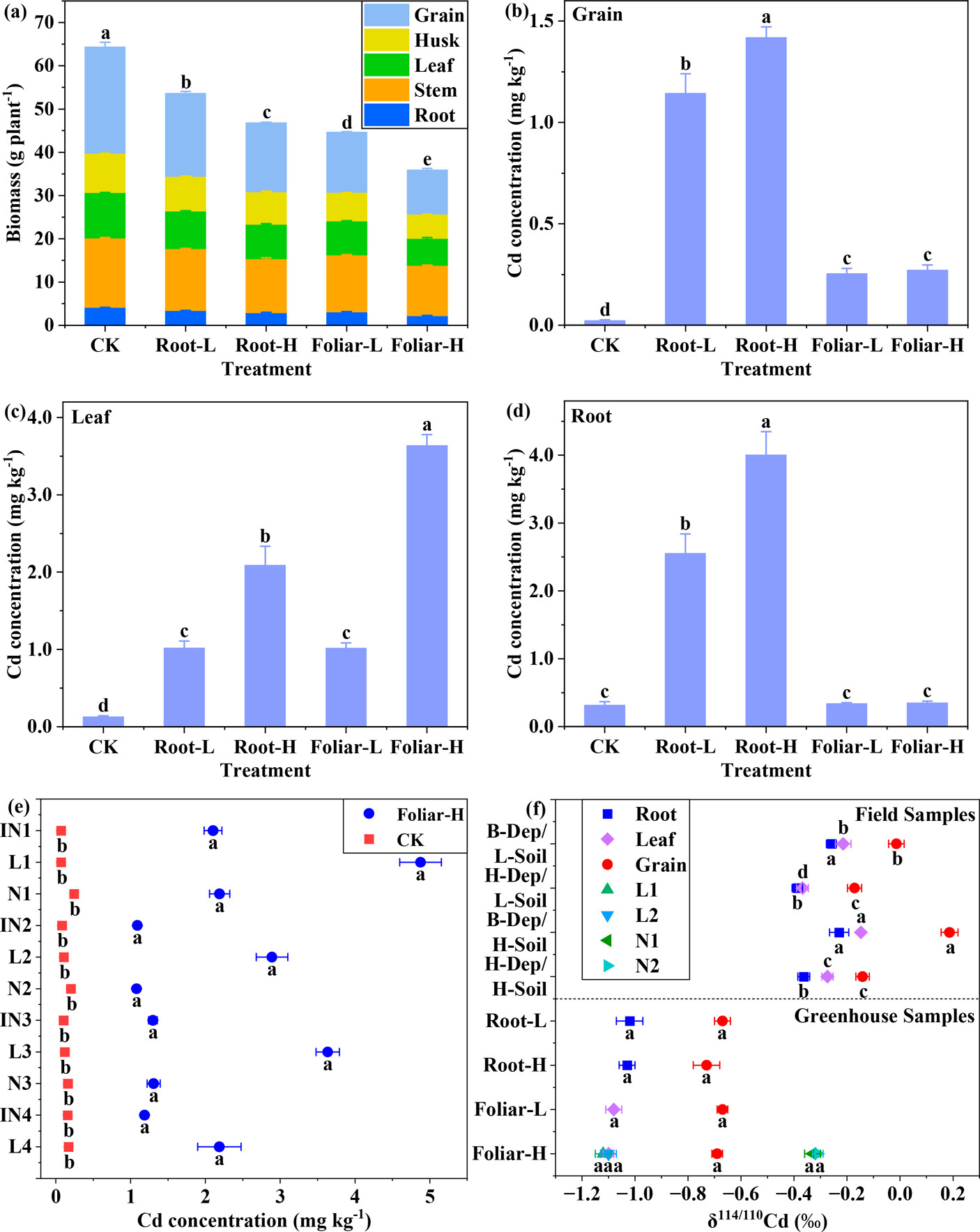
Figure. (a) Mean biomasses of rice tissues from five experiment pots. Cd concentrations (dry weight with standard deviations) in (b) grains, (c) leaves, (d) roots, and (e) three nodes, four internodes, and three leaves. (f) Cd isotopic composition of roots, leaves, nodes, and grains collected from five treatment pots. Ni represents the ith node. INi represents the ith internode. Li represents the ith leaf
Contact:
Zhou Jun
Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: zhoujun@issas.ac.cn
Web: http://english.issas.cas.cn/