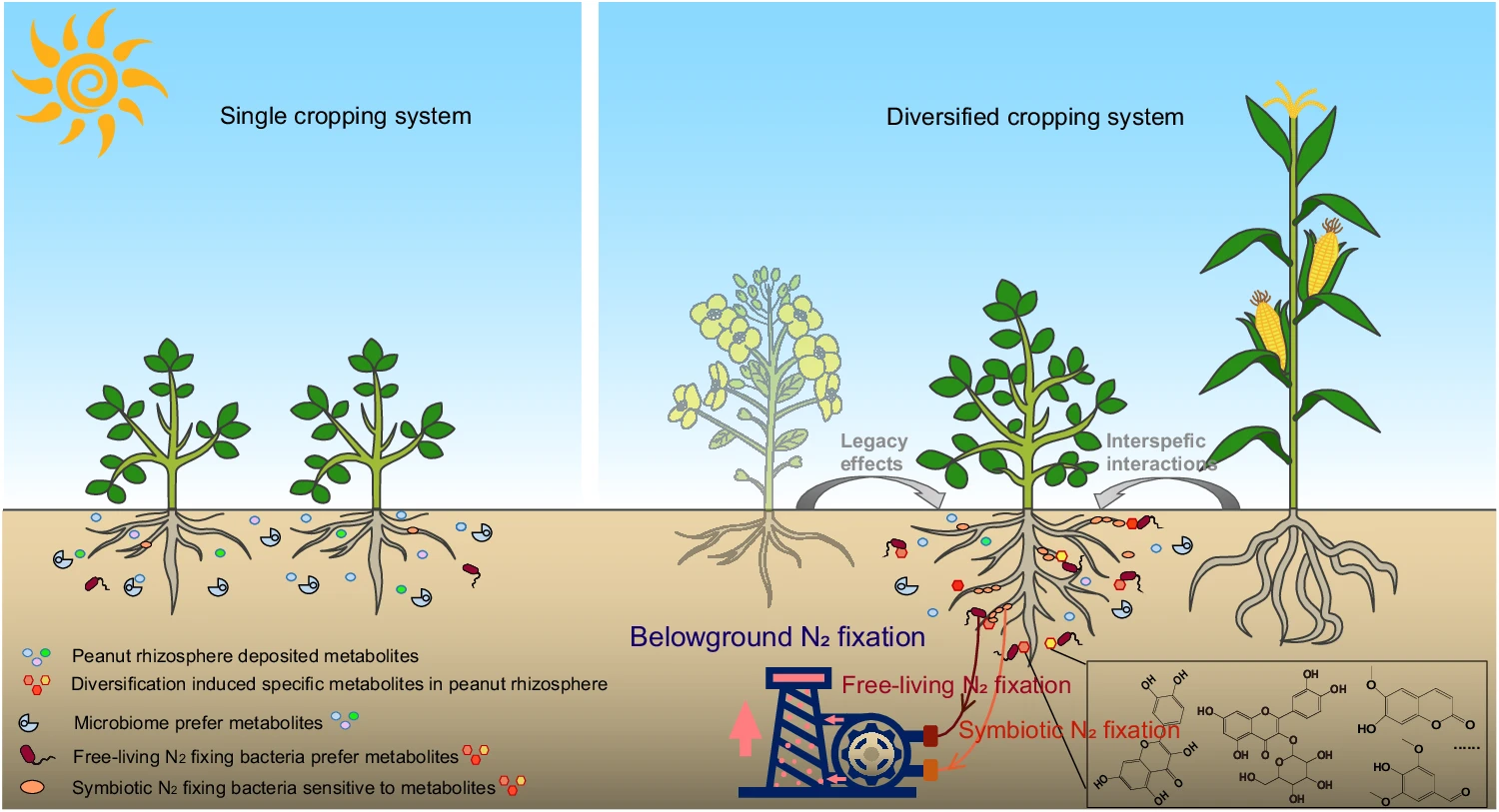
Legume rhizodeposition promotes nitrogen fixation by soil microbiota under crop diversification
Biological nitrogen fixation by free-living bacteria and rhizobial symbiosis with legumes plays a key role in sustainable crop production. Here, associate professor CHEN Yan and his team study how different crop combinations influence the interaction between peanut plants and their rhizosphere microbiota via metabolite deposition and functional responses of free-living and symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Based on a long-term (8 year) diversified cropping field experiment, they find that peanut co-cultured with maize and oilseed rape lead to specific changes in peanut rhizosphere metabolite profiles and bacterial functions and nodulation. Flavonoids and coumarins accumulate due to the activation of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathways in peanuts. These changes enhance the growth and nitrogen fixation activity of free-living bacterial isolates, and root nodulation by symbiotic Bradyrhizobium isolates. Peanut plant root metabolites interact with Bradyrhizobium isolates contributing to initiate nodulation. Their findings demonstrate that tailored intercropping could be used to improve soil nitrogen availability through changes in the rhizosphere microbiome and its functions.
Fig. Effect of crop diversification on metabolite deposition and biological N2 fixation in the leguminous rhizosphere.Contact:
CHEN Yan
Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Web: http://english.issas.cas.cn/